In this article, we will walk through the steps of deploying SonarQube on AWS ECS using Cluster.dev as an infrastructure installer. You’ll see how employing this tool can help quickly complete this otherwise arduous and time-consuming process.
SonarQube, developed by SonarSource, is an open-source platform dedicated to the ongoing assessment of code quality. The tool detects bugs and code smells across a variety of programming languages, employing automated reviews powered by static code analysis.
However, if you opt for a self-hosted SonarQube, it will require a robust and scalable infrastructure setup that is challenging to provision. In this case I’d recommend using AWS RDS for a resilient database and AWS ECS for a scalable computing layer. To initiate our infrastructure, we will use the Cluster.dev infrastructure installer.
The diagram below shows an infrastructure setup that we are going to build with Cluster.dev in this blogpost.
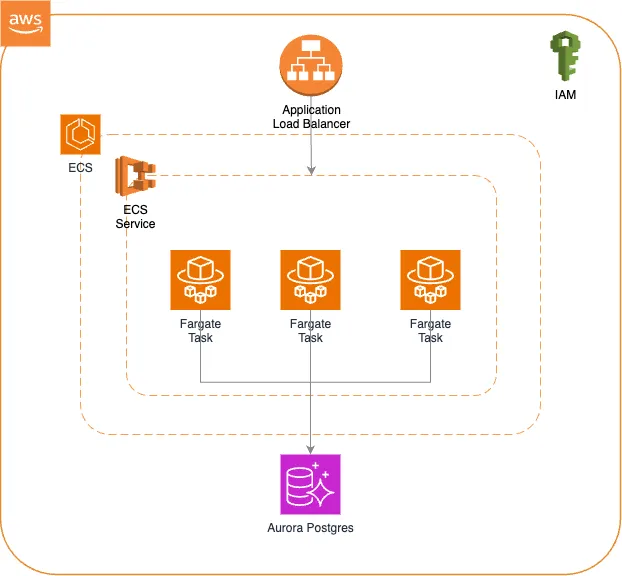
The high-level architecture diagram
Before proceeding into technical implementation, let’s briefly review the basics of Cluster.dev.
Cluster.dev main points
Explained below are the fundamentals of a Cluster.dev project.
- Unit: a unit represents an individual resource that is the structural element of our infrastructure setup (for example, a load balancer). Units can be implemented by various technologies, such as Terraform modules, Helm charts, Kubernetes manifests, Terraform code, Bash scripts, etc. Configuring a unit involves providing specific inputs, yielding distinct outputs for use, and reference by other units if needed.
- Stack template: a stack template is a set of units that will initiate and provision a certain infrastructure pattern, which in our case is the SonarQube deployment in ECS. With each unit representing a distinct tool, we can employ a variety of technologies to create complex infrastructure patterns within a stack template.
- Stack: a stack is a configuration file that defines the template’s setup and a set of variables that will be applied to the template.
- Project: a project can be defined as a high-level abstraction to store and reconcile different stacks. It also operates as a comprehensive variable repository for all stacks, allowing for passing global variables across different stacks within an infrastructure setup.
- Backend: a backend defines a location to store the Cluster.dev’s state, either locally or remotely.
The diagram below reveals how these building blocks are set up for SonarQube ECS deployment.
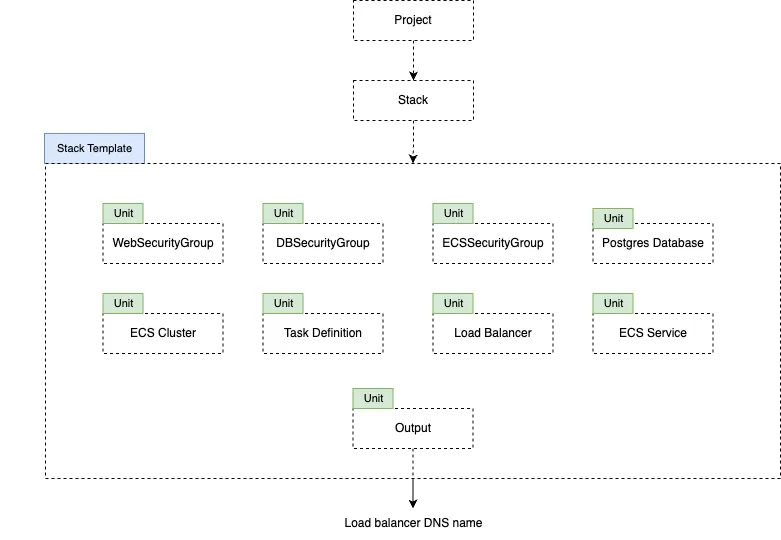 The layout of the Cluster.dev components for ECS deployment
The layout of the Cluster.dev components for ECS deployment
Technical implementation
Before implementing any infrastructure pattern, it’s crucial to identify the necessary resources as units and determine the appropriate technology for each. In this setup, we’ll use Terraform modules to create the following AWS resources:
- ECS Cluster
- ECS Task Definition
- ECS Service
- Load Balancer
- Postgres RDS Database
- Security groups for Database, Load balancer & ECS service
- Necessary IAM roles
Now let’s define all the necessary resources in the template.yaml file. The following YAML file encompasses all the AWS resources required for this setup. Notice how we’ve interconnected various Terraform modules to provision the necessary infrastructure. Additionally, we’ve employed several variables to ensure the repeatability of the infrastructure pattern for various use cases. The syntax for utilizing a variable is {{ .variables.<variable_name> }}, and we can reference the outputs of one unit in another using the {{ remoteState "this.<unit_name>.<attribute>" }} syntax.
Lastly, the Printer unit exposes the DNS name of the load balancer, enabling access to the deployed SonarQube application.
_p: &provider_aws
- aws:
region: {{ .variables.region }}
name: cdev-sonarqube
kind: StackTemplate
units:
- name: WebSecurityGroup
type: tfmodule
providers: *provider_aws
source: terraform-aws-modules/security-group/aws//modules/http-80
inputs:
name: 'WebSecurityGroup'
vpc_id: {{ .variables.vpc_id }}
ingress_cidr_blocks: ["0.0.0.0/0"]
- name: DBSecurityGroup
type: tfmodule
providers: *provider_aws
source: terraform-aws-modules/security-group/aws
inputs:
name: 'DBSecurityGroup'
vpc_id: {{ .variables.vpc_id }}
ingress_with_source_security_group_id:
- rule: "postgresql-tcp"
source_security_group_id: {{ remoteState "this.ECSSVCSecurityGroup.security_group_id" }}
- name: ECSSVCSecurityGroup
type: tfmodule
providers: *provider_aws
source: terraform-aws-modules/security-group/aws
inputs:
name: 'ECSSVCSecurityGroup'
vpc_id: {{ .variables.vpc_id }}
ingress_with_cidr_blocks:
- from_port: 9000
to_port: 9000
protocol: "tcp"
cidr_blocks: "0.0.0.0/0"
egress_with_cidr_blocks:
- from_port: 0
to_port: 0
protocol: "-1"
cidr_blocks: "0.0.0.0/0"
- name: Database
type: tfmodule
providers: *provider_aws
source: terraform-aws-modules/rds/aws
inputs:
engine: 'postgres'
engine_version: '14'
family: 'postgres14' # DB parameter group
major_engine_version: '14' # DB option group
instance_class: 'db.t4g.large'
identifier: 'sonar-database'
db_name: 'sonarqube'
username: 'sonar_user'
password: 'password'
publicly_accessible: true
allocated_storage: 5
manage_master_user_password: false
vpc_security_group_ids: [{{ remoteState "this.DBSecurityGroup.security_group_id" }}]
subnet_ids: [{{ .variables.subnet_1 }}, {{ .variables.subnet_2 }}]
- name: ECSCluster
type: tfmodule
providers: *provider_aws
source: terraform-aws-modules/ecs/aws
inputs:
cluster_name: 'sonar-cluster'
- name: ECSTaskDefinition
type: tfmodule
providers: *provider_aws
source: github.com/mongodb/terraform-aws-ecs-task-definition
inputs:
image: 'sonarqube:lts-community'
family: 'sonar'
name: 'sonar'
portMappings:
- containerPort: 9000
hostPort: 9000
protocol: 'tcp'
appProtocol: 'http'
command:
- '-Dsonar.search.javaAdditionalOpts=-Dnode.store.allow_mmap=false'
environment:
- name: SONAR_JDBC_URL
value: jdbc:postgresql://{{ remoteState "this.Database.db_instance_endpoint" }}/postgres
- name: SONAR_JDBC_USERNAME
value: sonar_user
- name: SONAR_JDBC_PASSWORD
value: password
requires_compatibilities:
- 'FARGATE'
cpu: 1024
memory: 3072
network_mode: awsvpc
- name: LoadBalancer
type: tfmodule
providers: *provider_aws
source: terraform-aws-modules/alb/aws
inputs:
name: 'sonarqube'
vpc_id: {{ .variables.vpc_id }}
subnets: [{{ .variables.subnet_1 }}, {{ .variables.subnet_2 }}]
enable_deletion_protection: false
create_security_group: false
security_groups: [{{ remoteState "this.WebSecurityGroup.security_group_id" }}]
target_groups:
ecsTarget:
name_prefix: 'SQ-'
protocol: 'HTTP'
port: 80
target_type: 'ip'
create_attachment: false
listeners:
ecs-foward:
port: 80
protocol: 'HTTP'
forward:
target_group_key: 'ecsTarget'
- name: ECSService
type: tfmodule
providers: *provider_aws
source: terraform-aws-modules/ecs/aws//modules/service
inputs:
name: 'sonarqube'
cluster_arn: {{ remoteState "this.ECSCluster.cluster_arn" }}
cpu: 1024
memory: 4096
create_task_definition: false
task_definition_arn: {{ remoteState "this.ECSTaskDefinition.arn" }}
create_security_group: false
create_task_exec_iam_role: true
assign_public_ip: true
subnet_ids: [{{ .variables.subnet_1 }}, {{ .variables.subnet_2 }}]
security_group_ids: [{{ remoteState "this.ECSSVCSecurityGroup.security_group_id" }}]
load_balancer:
service:
target_group_arn: {{ remoteState "this.LoadBalancer.target_groups.ecsTarget.arn" }}
container_name: sonar
container_port: 9000
- name: outputs
type: printer
depends_on: this.LoadBalancer
outputs:
sonar_url: http://{{ remoteState "this.LoadBalancer.dns_name" }}
With that, the complex part is over!
Let’s define the stack.yamlfile, which includes variables to configure the stack template. In this file, we’ve defined the configurations below as variables, so that we can easily adjust and reuse the existing AWS networking infrastructure.
- region: AWS region
- vpc_id: ID of VPC we need to deploy
- subnet_1: ID of subnet 1
- subnet_2: ID of subnet 2
If necessary, we can define more variables to make the stack template more flexible.
name: cdev-sonarqube
template: ./template/
kind: Stack
backend: aws-backend
variables:
region: {{ .project.variables.region }}
vpc_id: {{ .project.variables.vpc_id }}
subnet_1: {{ .project.variables.subnet_1 }}
subnet_2: {{ .project.variables.subnet_2 }}
We’ll utilize an S3 bucket to store the backend state of Cluster.dev. This can be configured in a backend.yaml file.
name: aws-backend
kind: Backend
provider: s3
spec:
bucket: {{ .project.variables.state_bucket_name }}
region: {{ .project.variables.region }}
Finally, we can define the project.yaml file to use this stack. For this infrastructure setup, we will use only a single stack. We can also define the global project variables within this file.
name: cdev-sonarqube kind: Project backend: aws-backend variables: organization: <org-name> region: <aws-region> state_bucket_name: <state-bucket-name> vpc_id: <vpc-id> subnet_1: <subnet1-id> subnet_2: <subnet2-id>
You can find full implementation details in this GitHub repository.
Deploying the infrastructure
Now we can deploy the stack with the Cluster.dev command cdev apply. Before executing the command make sure you have the Cluster.dev CLI installed.
Invoking the command brings forward the list of resourced to be created, as shown below:
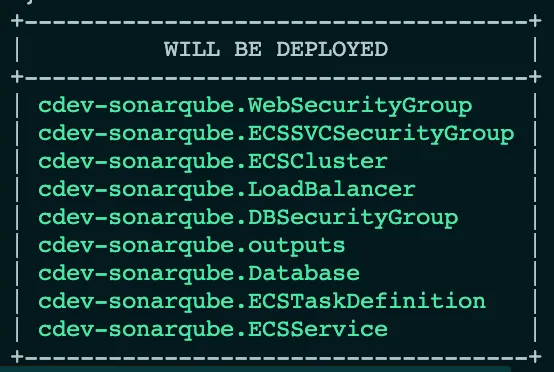
After the deployment is complete, the printer unit outputs the URL to access the deployed SonarQube application:
 Deployed SonarQube application
Deployed SonarQube application
As you can see, our deployment has auto-scaling enabled to scale out and scale in according to the incoming traffic.
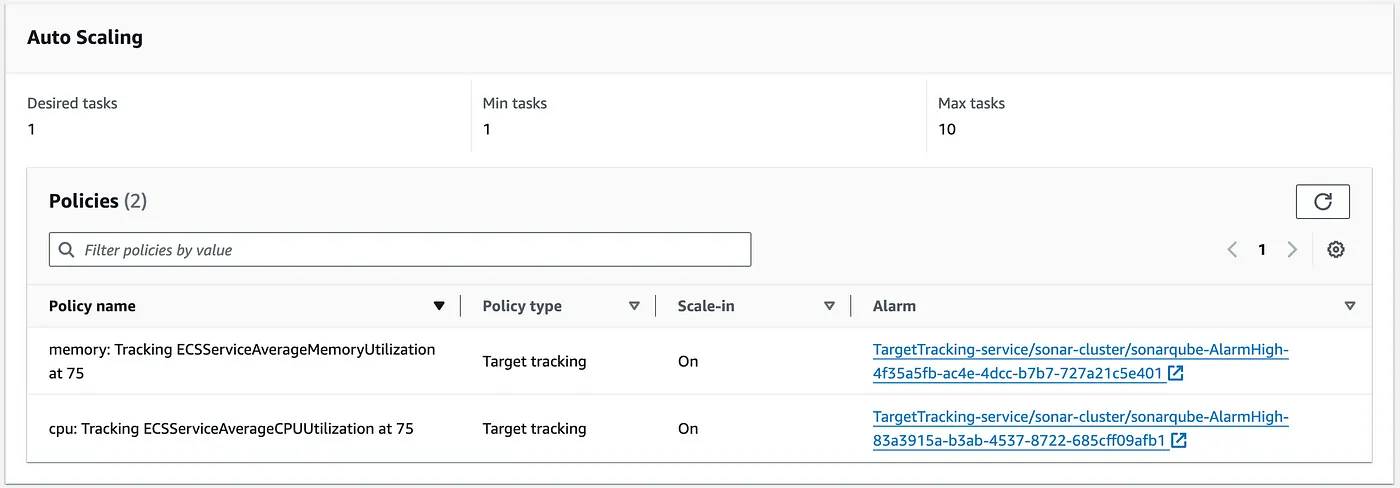 ECS auto-scaling policy
ECS auto-scaling policy
As shown in the diagram above, it scales out when the CPU and memory reach certain thresholds, up to a maximum of 10 tasks. These settings can be adjusted based on our specific requirements.
And there it is — the culmination of our efforts. With the templates prepared, you can configure them to fit the specific use case, enabling seamless and repeatable deployments. This streamlined approach ensures adaptability and efficiency, allowing for a quick and hassle-free setup whenever needed.
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve walked through the essential steps to deploy SonarQube on AWS ECS using Cluster.dev to cover its key aspects. By combining the capabilities of SonarQube with the simplicity of Cluster.dev, we’ve created a reliable and easily managed infrastructure for elevated code analysis and quality assurance practices.
 Schedule call
Schedule call


